Semaglutide has become a game-changer in weight management, helping millions achieve healthier weight.
Still, searching for a better weight-loss drug goes on for people with more complex needs.
Learn about tirzepatide, a groundbreaking weight-loss medication with double actions that surpasses conventional therapies.
Also, find the distinctions between tirzepatide vs. semaglutide to understand which option is better for safe and effective weight loss.
GLP-1 Drugs for Weight Loss Tirzepatide Vs. Semaglutide Show Head-to-head Results
What is Tirzepatide? And What is Semaglutide?
Tirzepatide and semaglutide are two groundbreaking anti-diabetic drugs that recently garnered FDA approval for chronic weight management.
Tirzepatide is the active ingredient in injectables Mounjaro and Zepbound, both commercial names developed by Eli Lilly. Mounjaro is primarily prescribed for diabetes management, while Zepbound is specifically designed for weight management.
Semaglutide is the active component in injectables Ozempic and Wegovy, along with the oral tablet Rybelsus, all developed by Novo Nordisk. These drugs were initially formulated for diabetes treatment but have been approved for weight management.
- Read: FDA Approves Wegovy (Semaglutide) for Chronic Weight Management
- Read: FDA Approves Zepbound (Tirzepatide) for Chronic Weight Management
The noteworthy similarity between tirzepatide and semaglutide is their mechanism of action, as both belong to the class of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs).
GLP-1 RAs are a class of drugs that effectively reduce blood sugar levels and energy intake by mimicking the actions of the natural hormone GLP-1.
Despite sharing this common foundation, tirzepatide distinguishes itself by being not only a GLP-1 RA but also a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP).
GIP is another class of drugs known for exerting weight loss effects. This dual-benefit characteristic makes tirzepatide stand out as a weight-loss drug that harnesses the synergistic effects of both GLP-1 and GIP pathways.
How Do Tirzepatide and Semaglutide Work?
Understanding GLP-1, GLP-1 RA, and GIP is crucial to comprehend the mechanisms underlying tirzepatide and semaglutide.
GLP-1 is an incretin hormone produced in the gut and released in response to food that plays a pivotal role in glucose homeostasis. It stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, slows gastric emptying, and promotes a feeling of fullness.
GLP-1 RAs are synthetic compounds that mimic the effects of GLP-1. By binding to the GLP-1 receptors, these agonists enhance insulin secretion, reduce glucagon release, and slow digestion, improving blood sugar control and reducing food intake.
GIP is another incretin hormone that stimulates insulin release in response to food intake. Similar to GLP-1, GIP also contributes to glucose homeostasis and energy regulation.
Semaglutide, as a GLP-1 RA, primarily operates through the GLP-1 pathway. It enhances insulin secretion, suppresses glucagon release, and induces a sense of satiety. The weight loss effects are primarily attributed to reduced food intake and slowed gastric emptying.
Tirzepatide, being a GLP-1 RA and GIP, capitalizes on the combined effects of both pathways. The GLP-1 component addresses blood sugar control and reduces energy intake, while the GIP component adds an extra weight loss benefit.
Tirzepatide Vs. Semaglutide for Weight Loss: A Comparison

A comprehensive study published in 2021 by The New England Journal of Medicine sought to illuminate the differences between tirzepatide vs. semaglutide concerning weight loss.
The study, an open-label, 40-week, phase 3 trial, meticulously assigned 1879 patients in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to receive either:
- Tirzepatide at doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg
- Semaglutide at a dose of 1 mg
This randomized patient distribution laid the groundwork for robust comparative analysis. The baseline characteristics reflected a diverse patient population, with a mean HbA1c level of 8.28%, a mean age of 56.6 years, and an average weight of 93.7 kg.
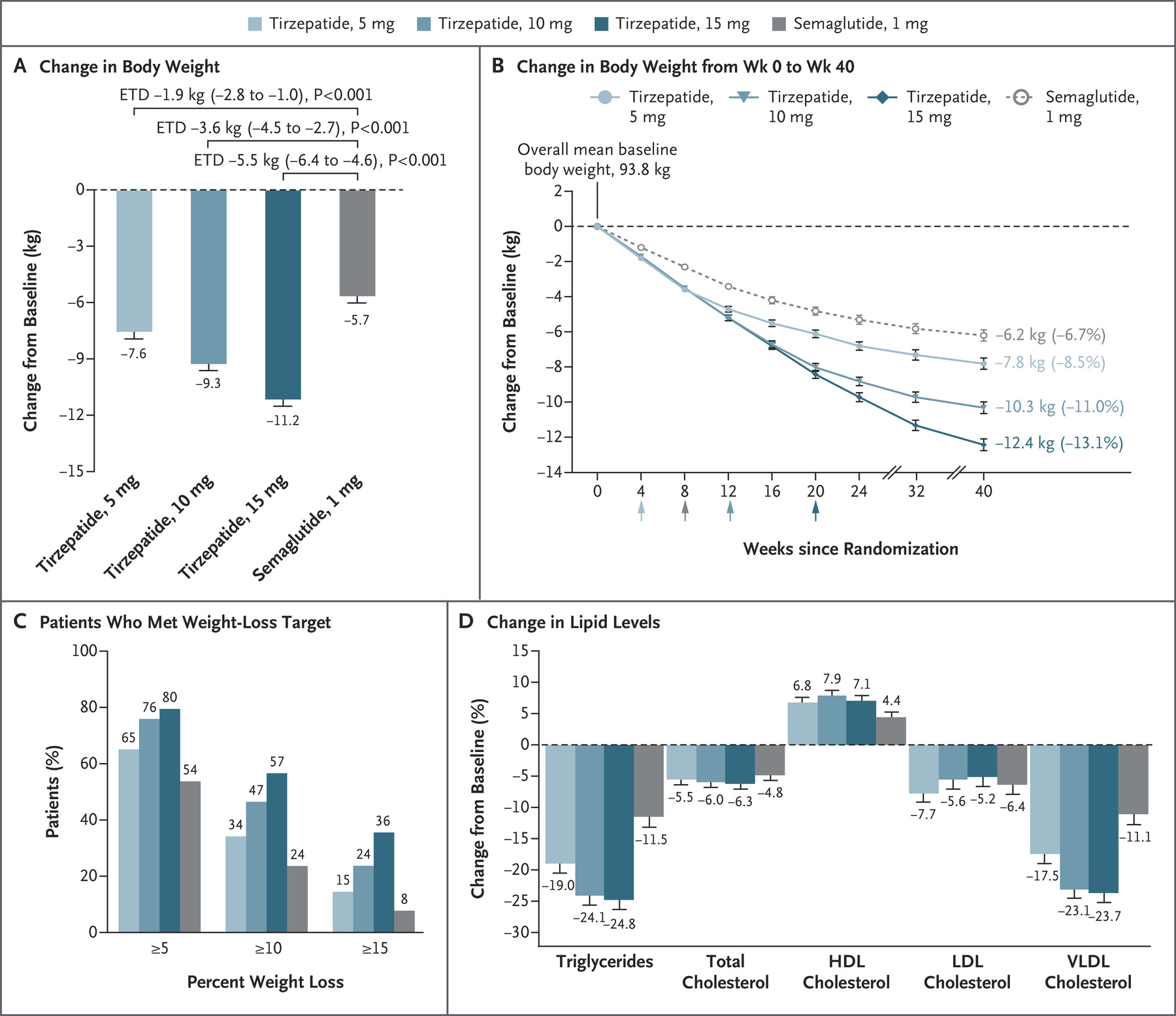
What emerged from this study was a clear and compelling trend — tirzepatide outperformed semaglutide across all doses in promoting weight loss.
After 40 weeks, the mean reductions in body weight were strikingly higher with tirzepatide at 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg, clocking in at −7.6 kg, −9.3 kg, and −11.2 kg, respectively, in stark contrast to the −5.7 kg seen with semaglutide.
Also, a higher proportion of patients on tirzepatide achieved a clinically significant weight loss of at least 10%, underscoring its efficacy in this realm.
Other Benefits: Glycemic Control, Triglyceride, and Cholesterol
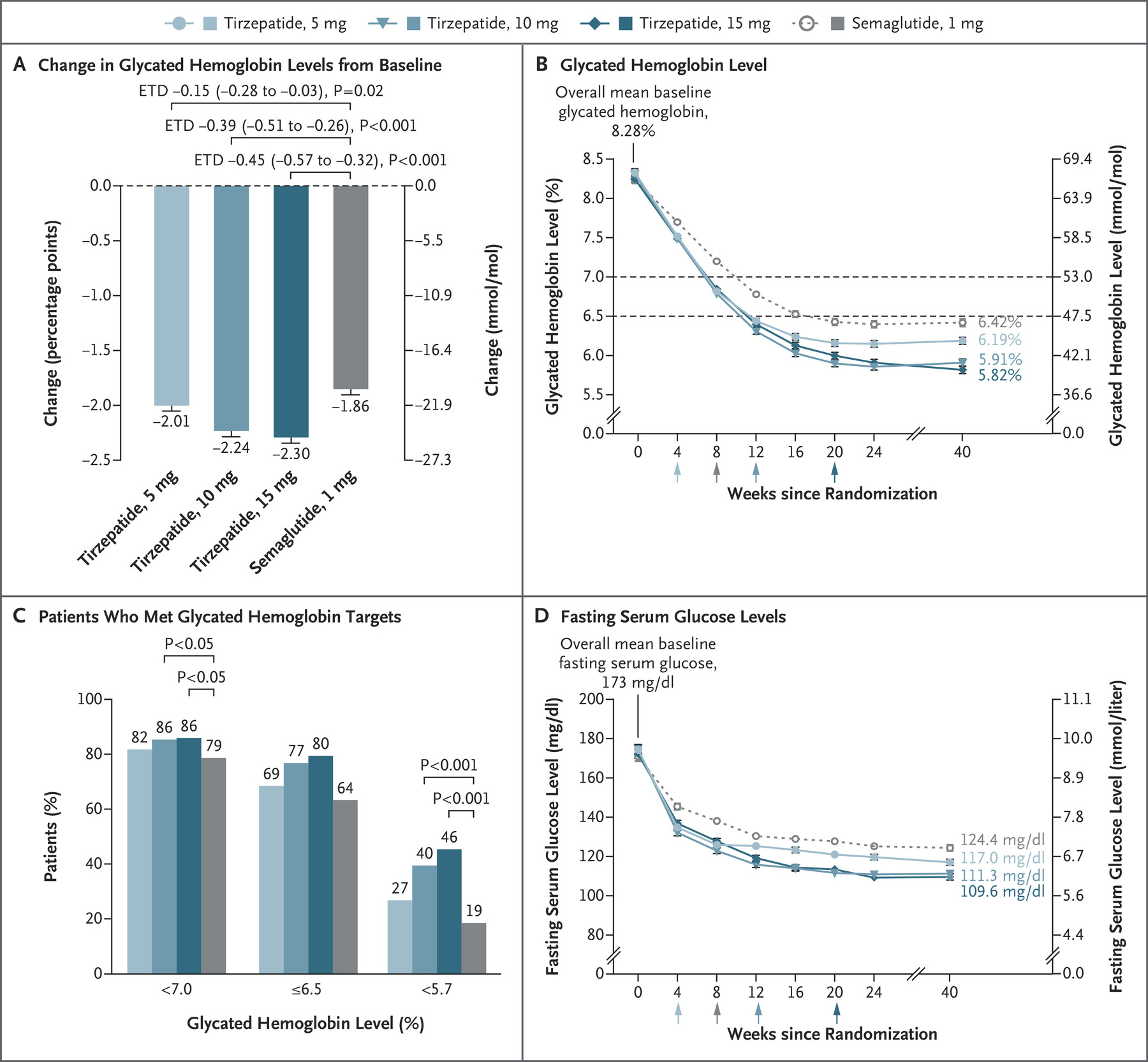
Beyond weight loss, the study looked at other health benefits of tirzepatide vs. semaglutide. Glycemic control, a cornerstone in diabetes management, was a focal point.
At 40 weeks, tirzepatide showcased its ability to bring about significant reductions in the mean HbA1c levels: −2.01%, −2.24%, and −2.30% for 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg doses, respectively, in contrast to the −1.86% observed with semaglutide.
Furthermore, in patients with a baseline HbA1c level above 8.5%, tirzepatide 15 mg surpassed semaglutide in mean reductions, indicating a potential advantage in glycemic control for patients with more challenging baseline conditions.
The study also investigated the effects of tirzepatide vs. semaglutide on lipid metabolism.
At 40 weeks, patients on tirzepatide experienced lower triglyceride and serum very-low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels and higher high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels than their semaglutide counterparts.
These findings not only underscored the multi-pronged benefits of tirzepatide but also hinted at its potential to positively influence lipid profiles. This aspect holds paramount importance in overall cardiovascular health.
Tirzepatide Vs. Semaglutide Side Effects
While the efficacy of tirzepatide and semaglutide is paramount, safety considerations are equally critical in evaluating the viability of pharmaceutical interventions.
The percentages of patients reporting adverse events were similar between the two treatment groups, suggesting a comparable overall incidence of adverse effects.
However, a notable divergence emerged concerning serious adverse events — a higher number was observed among patients receiving tirzepatide.
The most frequently reported adverse events were gastrointestinal issues, which are typical with GLP-1 receptor agonists. Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and decreased appetite featured prominently in both tirzepatide and semaglutide groups.
Hypoglycemia, a concern with anti-diabetic medications, was more frequently reported in patients receiving tirzepatide compared to those on semaglutide.
Although pancreatitis was reported in both groups, no cases were classified as severe.
Hypersensitivity reactions and injection-site reactions were also reported. While occurring in a minority of patients, these events were generally mild to moderate in severity.
How Much Weight Can You Lose With Tirzepatide?

The weight loss potential of tirzepatide, as evidenced by the study above, showcases impressive results. After the 40-week trial, tirzepatide demonstrated substantial efficacy in promoting weight loss across various doses.
Patients receiving tirzepatide experienced mean reductions in body weight ranging from −7.6 kg to −11.2 kg, outperforming semaglutide.
How Long Does It Take for Tirzepatide to Work?
In the study, the 40-week duration provided an extensive evaluation of tirzepatide’s effectiveness. Notably, the impact was evident within a relatively short time frame.
As early as 4-6 weeks into the trial, individuals noticed observable reductions in body weight. This quick action underscores tirzepatide’s ability to initiate its effects promptly.
Who Should Take Tirzepatide? Who Should Not?
The eligibility criteria for tirzepatide are based on a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare provider, considering factors such as:
- Medical history
- Current health conditions
- The presence of diabetes or obesity
In general, GLP-1 receptor agonists like tirzepatide are often prescribed for individuals with a BMI of 30 or higher, especially if they have obesity-related comorbidities, or for those with a BMI of 27 or higher if they have additional risk factors.
Specific contraindications must also be taken into account:
- Thyroid Tumors: Avoid tirzepatide if there is a personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2.
- Pancreatic and Gastric Issues: Caution if there is a history of pancreatitis or severe gastrointestinal disease.
- Combination Use: Do not use tirzepatide with Mounjaro or other GLP-1 agonists.
- Allergic Reactions: Avoid tirzepatide if there is a history of severe allergic reactions to tirzepatide.
- Additional Warnings: Discuss with a healthcare provider if experiencing symptoms related to warnings for pancreatitis, gallbladder issues, hypoglycemia, acute kidney injury, diabetic retinopathy, or suicidal thoughts.
Outlook: More Research is Required
Tirzepatide and semaglutide represent a new era in the treatment of diabetes and obesity. While both drugs share a foundation in GLP-1 agonism, tirzepatide’s additional GIP component further distinguishes it as a dual-action weight loss medication.
The study’s detailed investigation into tirzepatide and semaglutide revealed the comparative effectiveness of these drugs in weight loss and their nuanced impacts on glycemic control, lipid metabolism, and safety profiles.
These findings provide a robust foundation for clinicians to make informed decisions tailored to the unique needs of individual patients, paving the way for a more personalized and practical approach to diabetes and weight management.
References
Frías J. et al. (2021). Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. The New England Journal of Medicine.
UP NEXT:

